Overview of U.S. Fixed Broadband Competition Landscape
The U.S. broadband market is entering a transformative competitive phase as fiber pushes deeper into legacy territories, fixed wireless scales across more markets, and public funding accelerates network expansion. For broadband organizations, the key question is no longer simply where service exists, but where competitive pressure – and ROI – will shift next.
This Broadband in America report highlights the major dynamics reshaping the fixed broadband competition landscape across fiber, cable and fixed wireless.
Fiber’s competitive expansion: markets transition to overbuild
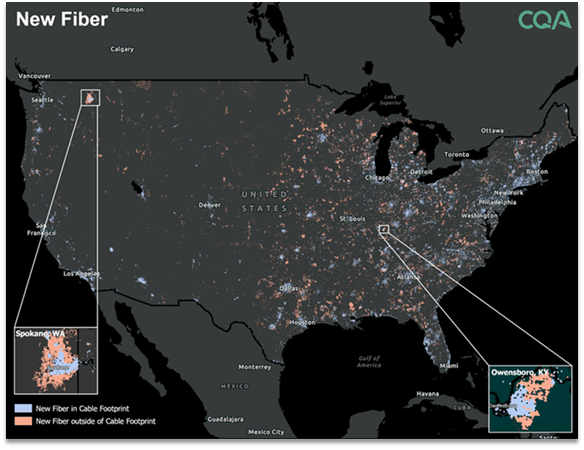
Fiber remains the core long-term growth engine of fixed broadband, attracting the majority of recent capital investment. While most new fiber construction continues reaching previously unserved homes, the nature of growth is changing as markets transition from one fiber provider markets to competitive overbuilds.
Today, approximately 28% of new fiber is now being built to homes already served by both fiber and cable providers, demonstrating intensifying fixed broadband competition in dense, urban markets.
Provider strategy divergence: large vs. small providers
Large and small fiber providers are pursuing distinct competitive strategies. Smaller providers tend to be more aggressive overbuilders, with approximately 40% of their new builds now targeting second-fiber markets – up from 18% in 2022. Their strategies and reasons vary, from defending a customer base served by an alternative technology to geographical constraints.
Cable’s competitive position: large footprint, shifting outcomes
Large cable operators remain central players in fixed broadband competition, with expansive footprints and national penetration rates above 50%. New cable company expansion often includes fiber as they race to keep customers happy with deeper fiber penetration.
However, cable providers are experiencing subscriber losses despite continued network expansion, suggesting incremental performance improvements do not automatically produce incremental customers in newly competitive markets.
Fixed wireless and future competitive dynamics: licensed vs. unlicensed
Licensed fixed wireless remains a credible alternative in suburban and rural markets, while unlicensed fixed wireless service areas are shrinking where wireline overbuilds occur.
As BEAD funding programs roll out and providers continue modernizing networks, fixed broadband competition will intensify further. Technology competition continues to reshape customer outcomes across all fixed broadband platforms, with fiber adoption expected to further pressure cable for subscriber share.
For the complete analysis, click here to read the full Broadband in America Fixed Broadband Competition Focus report.